

Atlas of Human Anatomy in Cross Section: Section 6. Pelvis, Perineum, Hip, and Upper Thigh
Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Jean J. Jew, M.D., and Paul
C. Reimann, B.S.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
|
Upper Left Quadrant |
Lower Left Quadrant |
Lower Right Quadrant |
Upper Right Quadrant |
|
1. Urinary bladder |
15. Gluteus medius m. |
28. Rectum |
44. Tensor fascia lata m. |
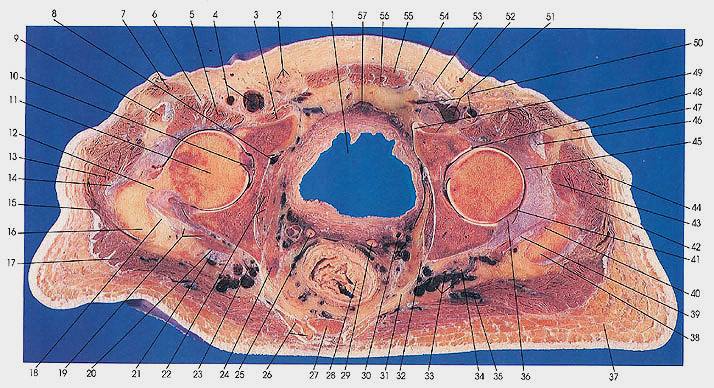
This section passes through the lowest part of the fifth sacral vertebra (27), the cornu and transverse process of the first coccygeal vertebra (26), spine of the ischium (24), and the lower part of the right acetabulum and upper part of the left (36). The head (11), neck (12), and greater trochanter (16) of the femur are seen on the right side.
The femoral artery and vein (4, 51) are in the fossa ovalis, and the spermatic cords (2, 53) are presently in a medial position.
The great saphenous vein (52) is seen for the first time in this section.
The common tendon of the obturator internus and gemelli muscles (18, 39) and its
insertion (40) onto the medial side of the greater trochanter (38) in front of the trochanteric fossa (38) of the femur are seen on both the right and left sides.
Gluteus medius muscle (15) is not seen after this cut, but the coccygeus muscle (31) makes its first appearance.
The relationship between the superior and inferior gemelli muscles (19, 20) and the sciatic nerve (21) is seen in this section. The sciatic nerve (21) leaves the pelvis via the greater sciatic foremen, usually but not always beneath the piriformis muscle and over the gemelli muscles.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2025 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/