

Plate 17.353 Striatum and Thalamus
Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Paul M. Heidger,
Jr., Ph.D.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
Human, 10% formalin, Weigert's hematoxylin (Loyez), 1.1 x.
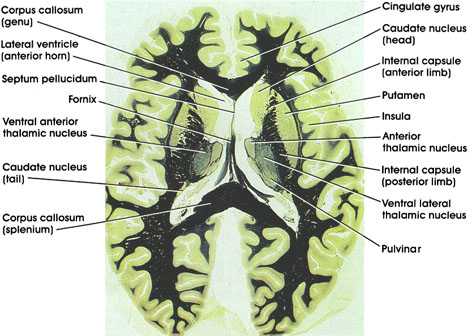
Corpus callosum: C-shaped bundle of heavily myelinated fibers. Connects the two hemispheres. Important in interhemispheric transfer of information. Section is through the genu (anterior) and splenium (posterior) parts of the corpus callosum.
Cingulate gyrus: A component of the limbic lobe. Located dorsal to the corpus callosurn on the medial surface of the hemisphere.
Caudate nucleus: C-shaped mass of gray matter closely related to the lateral ventricle. A component of the basal ganglia and thus concerned with motor control. Section shows the head of the caudate (anterior) and the much smaller tail (posterior).
Internal capsule: A massive bundle of myelinated fibers conveying motor and sensory impulses from and to the cerebral cortex. The anterior limb separates the caudate nucleus and putamen, whereas the posterior limb separates the putamen and thalamus.
Putamen: A component of the basal ganglia. Concerned with motor control.
Insula: Also referred to as the island of Reil. Lies deep in the sylvian fissure. Concerned with autonomic function.
Anterior thalamic nucleus: Belongs to the anterior group of thalamic nuclei. Has reciprocal connections with the mamillary body via the mamillothalamic tract and with the cingulate gyrus via the internal capsule. Considered part of the limbic system and thus plays a role in emotional behavior and memory.
Ventral lateral thalamic nucleus: Traversed by bundles of myelinated fibers. Belongs to the lateral group of thalamic nuclei. Relay thalamic nucleus for cerebellar fibers to the motor cortex. Reciprocally connected with the primary motor cortex. Concerned with motor control.
Pulvinar: One of the lateral group of thalamic nuclei. Has reciprocal connections with the medial and lateral geniculate bodies caudally and the association parietal, temporal, and occipital cortices rostrally. involved in several neural functions, including vision, audition, speech, and pain.
Fornix: A paired C-shaped fiber tract connecting the hippocampus with several brain regions, including the mamillary body, anterior thalamic nucleus, septal nuclei, and cingulate gyrus.
Lateral ventricle (anterior horn): Note characteristic bulge of head of caudate into the anterior horn.
Septum pellucidum: Separates the two cavities of the lateral ventricle. May contain a cavity, cavurn septi pellucidi.
Ventral anterior thalamic nucleus: One of the lateral group of thalamic nuclei. Characteristically traversed by heavily myelinated fiber bundles. Receives fibers from the basal ganglia and projects to the motor cortex. The posterior limb separates the thalamus from the putamen.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
Anatomy Atlases is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. 
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/