

Plate 17.335 Pons
Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Paul M. Heidger,
Jr., Ph.D.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
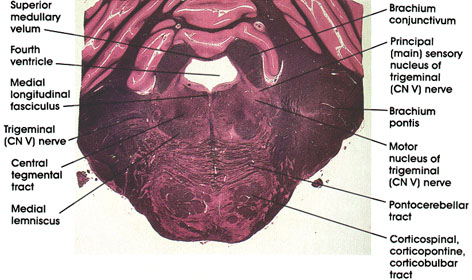
Human, 10% formalin, Pal-Weigert, 2.4 x.
Fourth ventricle: The anterior part of the fourth ventricle overlying the pons.
Brachium conjunctivum: Massive outflow tract from the cerebellum seen at this level prior to decussation. Lesions in this area will result in a disorder of coordinated movement. Note the change in position of this structure in more rostral sections (see Plates 337, 338 and 339).
Principal (main) sensory nucleus of trigerninal (CN V) nerve: Located lateral to the motor nucleus of the trigeminal. Receives touch sensations from the ipsilateral face via the trigeminal nerve.
Motor nucleus of trigerninal (CN V) nerve: Located in the dorsal part of the tegmentum. Axons form the motor root of the trigerninal nerve and supply muscles of mastication, and the tensor tympani, tensor palati, mylohyoid, and the anterior belly of the digastric muscles.
Brachium pontis: Also known as the middle cerebellar peduncle. A massive bundle of fibers connecting the basal portion of the pons with the cerebellum. Contains pontocerebellar fibers.
Pontocerebellar tract: Axons of pontine nuclei destined for the cerebellum via the brachium pontis.
Corticospinal, corticopontine, corticobulbar tracts: Long descending fiber system originating in the cerebral cortex. Sectioned transversely as it passes through the basal portion of the pons. Note the horizontally oriented pontocerebellar tract.
Medial lemniscus: Continuation of the same system seen in more caudal levels.
Trigeminal nerve: Sensory-motor cranial nerve. Seen coursing in the lateral part of the pons.
Central tegmental tract: Compact fiber bundle located in the tegmenturn of the pons. Carries fibers from midbrain tegmentum, red nucleus, and periaqueductal gray matter to the inferior olivary complex.
Medial longitudinal fasciculus: Ascending component of a fiber system originating in vestibular nuclei and destined to synapse with neurons in nuclei of extraocular movement (CN III, IV, and VI). Concerned with control of eye movement.
Superior medullary velum: Forms the anterior (superior) part of the roof of the fourth ventricle.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
Anatomy Atlases is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. 
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/