

Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Paul M. Heidger,
Jr., Ph.D.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
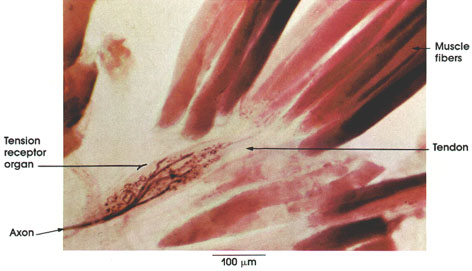
Rabbit, formic acid-gold chloride, 162 x.
Axon: Myelinated axons break into primary, secondary, and tertiary branches. Unmyelinated branches from these axons wind around and in between tendon fascicles.
Tendon: Collagenous connective tissue bundle joined to several muscle fibers.
Muscle fibers: Skeletal (striated) muscle fibers.
Tension receptor organ (Golgi tendon organ): Discharges electrical impulses in response to tension on the tendon produced by either muscular contraction or muscle stretch. Provides information about the state of the muscle tension that determines in part the response of the central nervous system in the appropriate use of the muscle or muscles for precise motor function. Afferent impulses from Golgi tendon organs are conveyed to the central nervous system via lb nerve fibers, which exert presynaptic inhibition on the la nerve fibers originating in the muscle spindle.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
Anatomy Atlases is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. 
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/