

Aorta
Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Paul M. Heidger,
Jr., Ph.D.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
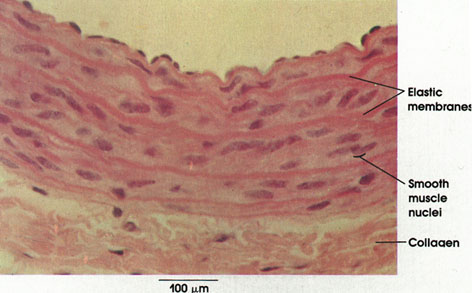
Rat, Helly's fluid, H. & E., 162 x.
Compare this general staining method with that used in Plate 35. The general method used in this preparation allows differentiation of the various vessel wall components only by the variations in the intensity of staining. The pronounced eosinophilia of the elastic fibers reflects their high content of basic amino acids. See also Plates 152 and 156.
Elastic membranes: Abundant in the media of elastic arteries. The elastic fibers anastomose to form a fenestrated "membrane," which is circularly arranged in layers.
Smooth muscle nuclei: Smooth muscle fibers are located between the elastic fiber networks. Circularly disposed.
Collagen: In the adventitia, collagen forms a loose irregular connective tissue layer surrounding the blood vessel. Elastic fibers, not distinguishable by this method, are also found in this connective tissue coat.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
Anatomy Atlases is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. 
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/