

Atlas of Human Anatomy in Cross Section: Section 7. Lower Limb
Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Jean J. Jew, M.D., and Paul
C. Reimann, B.S.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
|
Upper Left Quadrant |
Lower Left Quadrant |
Lower Right Quadrant |
Upper Right Quadrant |
|
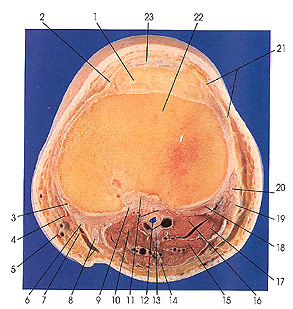
1. Infrapatellar fat pad |
3. Tibial collateral ligament |
12. Popliteal v. and a. |
21. Lateral patellar retinaculum and iliotibial tract |
This section passes just below the articular surface of the tibia and slightly above the tibiofibular articulation (seen in next cut). It cuts the tendons of biceps femoris (20), semitendinosus and semimembranosus (8), sartorius (4, 7), and gracilis (6). The sartorius muscle (but not its tendon) makes its last appearance, and the popliteus muscle (11) makes its first appearance in this section.
The lateral patellar retinaculum (21) is discussed with Plate 7. 11. The medial patellar retinaculum (2) is derived from the tendon of vastus medialis. It is attached to the patella along its medial border and passing along its sides to the tibia it attaches onto the oblique ridge and extends as far as the tibial collateral ligament (3). The medial patellar retinaculum extends distally beyond the oblique ridge to blend with the periosteum of the shaft of the tibia. The patellar retinaculum also becomes inseparably joined with the fibrous membrane of the articular capsule.
The fibular (18) and tibial (3) collateral ligaments are discussed with Plate 7.14.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2025 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/