

Atlas of Human Anatomy in Cross Section: Section 2. Neck, Shoulders, Upper Arm, and Upper Thorax (Lungs)
Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Jean J. Jew, M.D., and Paul
C. Reimann, B.S.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
|
Upper Left Quadrant |
Lower Left Quadrant |
Lower Right Quadrant |
Upper Right Quadrant |
|
1. Laryngopharynx |
13. Middle scalene m. |
25. Interscapular fat |
45. Dorsal root ganglion, C5 |
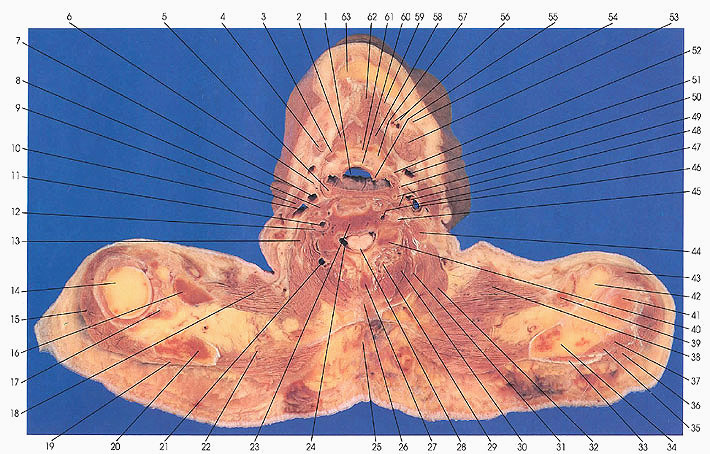
This section passes through the mandible (63), hyoid bone (5, 49, 57, 61), submandibular gland (4, 53), laryngopharynx (1), sixth cervical vertebra (23), trapezius muscle (18, 38), scapular spine (20, 34), humeral head (14), and clavicle (16, 39). The hyoid bone with its greater and lesser horns (49, 57) and the epiglottic cartilage (60) are seen.
Note the cervical enlargement of the spinal cord (28). The cervical enlargement results from the accumulation of neurons and their processes, which form the brachial plexus of nerves supplying the arm, forearm, and hand. In the thoracic region the spinal cord becomes smaller in diameter.
The vertebral arteries (11,47) are entering the transverse foramina of the sixth cervical vertebra. The vertebral artery enters the sixth foramina in about 87% of cases, the seventh foramina in 5%, and the fifth foramina in about 7%.
Identifiable neck muscles include levator scapulae (32), longissimus capitis and cervicis (31), semispinalis capitis (30), multifidus (29), anterior (49) and middle (13, 44) scalenes, and sternocleidomastoid (9).
Muscles of the shoulder region include trapezius (18, 38), deltoid (15, 43), triceps brachii (17, 37), teres minor (36), supraspinatus (35), and infraspinatus (33).
The spine of the scapula (20, 34), acromion process of scapula (42), clavicle (16), and humeral heads (14, 41) are seen. The transverse cervical artery and vein and the spinal accessory nerve are seen entering the trapezius muscle (22).
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2025 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/