

Atlas of Human Anatomy in Cross Section: Section 1. Head and Neck
Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Jean J. Jew, M.D., and Paul
C. Reimann, B.S.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
|
Upper Left Quadrant |
Lower Left Quadrant |
Lower Right Quadrant |
Upper Right Quadrant |
|
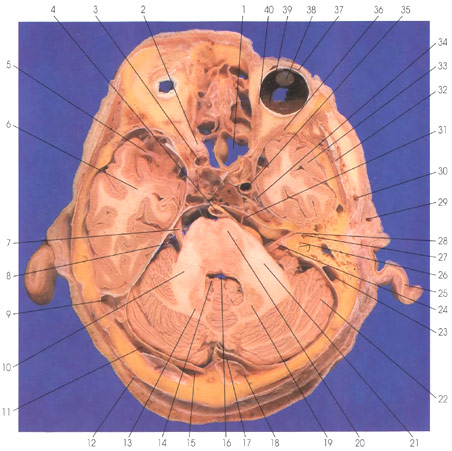
1. Sphenoid sinus |
7. Trigeminal nerve |
16. Fourth ventricle |
29. Superficial temporal a. |
This is a section (looking down) through the orbit, temporal lobe, cerebellum, and pons. On each side of the midline anteriorly in the section is a spheroid sinus (1). Within the orbital cavity, the following structures are seen: medial (40) and lateral (36) rectus muscles, and within the globe the retina (39), lens (38), and conjunctive (37). The optic nerve (2) is seen exiting from the orbital cavity in close proximity to the internal carotid artery (3). The temporal lobe (6, 33) is in the middle cranial fossa. Branches of the middle cerebral artery (5) are in the lateral (sylvian) fissure. Medial to the temporal lobe are the trigeminal nerve and ganglion (34) in Meckel's cave and the internal carotid artery (35). Between the temporal lobe (33) and the cerebellar hemisphere (22) are the vestibule (27) and semicircular canals (26) of the bony labyrinth. In the posterior fossa are the cerebellum (13, 19, 22) and the pons (20). The fourth ventricle (16) is seen between the cerebellum and pons. The choroid plexus (14) is seen in the roof of the fourth ventricle (16). Within the pons, the basis pontis (20) is ventrally located. The middle cerebellar peduncles (brachium pontis) (10, 21) connect the basis pontis (20) with the cerebellum (22). The basilar artery (4) lies in a groove on the ventral surface of the basis pontis (20). The vestibulocochlear (24), facial (8, 24), and trigeminal (7) nerves exit from the lateral surface of the pons, whereas the abducens nerve (31) exits from the inferior surface of the pons. Within the deep white matter of the cerebellar hemisphere (22) is the dentate nucleus of the cerebellum (13,19). Several venous sinuses are seen in this section: the sigmoid sinus (9,23), transverse sinus (11,15,17), and the confluence of sinuses (18). Outside the cranial cavity, the following structures are seen: the auricle (25), superficial temporal artery (29, 30), the occipital artery (12), and temporalis muscle (32). Within the cranial cavity, the facial and vestibulocochlear nerves (28) are seen within the internal auditory meatus of the temporal bone.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2025 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/