

Atlas of Human Anatomy in Cross Section: Section 1. Head and Neck
Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Jean J. Jew,
M.D., and Paul C. Reimann, B.S.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
|
Upper Left Quadrant |
Lower Left Quadrant |
Lower Right Quadrant |
Upper Right Quadrant |
|
1. Anterior cerebral a., brs. |
13. Hippocampus |
19. Vermis of cerebellum |
23. Superior temporal gyrus |
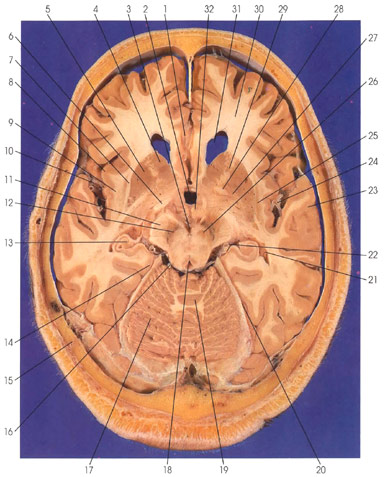
This is a section through the basal ganglia, midbrain, and cerebellum. The three principal basal ganglia, the caudate (4), putamen (5), and globus pallidus (27), are seen. The three nuclei are collectively known as the corpus striatum. The anterior limb of the internal capsule (29) separates the head of the caudate nucleus (4) from the putamen (5). The putamen (5) is lateral and ventral to the head of the caudate (4). The globus pallidus (27) is medial to the putamen (5). Lateral to the putamen is the external capsule (7), claustrum (25), and the extreme capsule (9). The head of the caudate nucleus (4) forms part of the lateral wall of the frontal (anterior) horn of the lateral ventricle (31). In close proximity to the globus pallidus (27) is the anterior commissure (28), an interhemispheric commissural bundle. Ventral to the third ventricle (2) are the mamillary bodies (32) of the hypothalamus. Caudal to the mamillary bodies (32) is the midbrain. Within the midbrain, the following structures are discernible: aqueduct of Sylvius (18), red nucleus (26), substantia nigra (12), and cerebral peduncle (11). The interpeduncular fossa (3) lies on the ventral surface of the midbrain between the two cerebral peduncles (11). Close to the cerebral peduncles (11) is the optic tract (6). In the subarachnoid space around the midbrain are the following arteries: posterior cerebral (22) and superior cerebellar (16). Caudal to the midbrain is the cerebellum with its midline vermis (19) and lateral cerebellar hemispheres (17). The tentorium cerebelli (20) is a dural fold that separates the cerebellum from the occipital cortex. The temporal (inferior) horn of the lateral ventricle (21) is seen with the hippocampus (13) protruding into its medial wall. The hippocampus (13) is continuous with the parahippocampal gyrus (14), which infolds into the temporal (inferior) horn of the lateral ventricle (21) to form the hippocampus (13). The superior temporal gyrus (23) is seen ventral to the lateral (sylvian) fissure (10). Branches of the middle cerebral artery (24) are seen in the lateral (sylvian) fissure (10). The insula (island of Reil) (8) lies in the depth of the lateral (sylvian) fissure (10). In the interhemispheric fissure rostrally, branches of the anterior cerebral artery (1) are seen. Other structures seen in this section are the white matter core of the frontal lobe (30) and lambdoid suture (15) of the calvarium.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2025 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/