

Illustrated Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation: Opus II: Cardiovascular System
Ronald A. Bergman, PhD
Adel K. Afifi, MD, MS
Ryosuke Miyauchi, MD
Peer Review Status: Internally Peer Reviewed
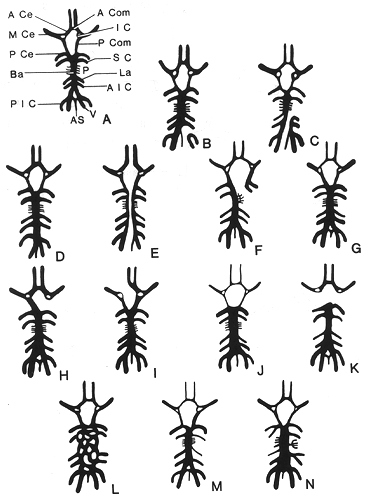
Based on a study of 600 brains.
A: Normal cerebral arterial circle and associated vessels. A Com, anterior communicating; A Ce, anterior cerebral; M Ce, Middle cerebral; P Ce, posterior cerebral; IC, internal carotid stump; P Com, posterior communicating; SC, superior cerebeilar; Ba, basilar; La, labyrinthine; AIC, anterior inferior cerebellar; PIC, posterior inferior cerebellar; V, vertebral; AS, anterior spinal; P, pontine.
B, C: Failure of vertebral artery to unite with the basilar artery (extremely rare anomaly).
D: Inferior union of vertebral arteries to form basilar artery.
E: Double basilar artery with absence of anterior communicating artery (1st description of this anomaly).
F: Failure of left posterior communicating artery to unite with rostral end of basilar artery; all pontine branches arise from left side of basilar artery.
G: A specimen showing underdeveloped anterior cerebral, anterior communicating, and left posterior communicating arteries.
H: Absence of left posterior communicating artery.
I: Both anterior cerebral arteries are related only to the left internal carotid artery.
J: Specimen from a microcephalic idiot showing attenuation of internal carotid arteries and their branches, and a large saccular basilar artery.
K: Absence of both posterior communicating arteries.
L: A plexiform basilar artery (1st description of this anomaly).
M: Specimen showing difference in size of internal carotid, posterior communicating, middle, and anterior cerebral arteries, with right side underdeveloped.
N: A composite drawing showing several variations found in different specimens: (a) anterior inferior cerebellar and internal auditory arteries arise as branches from a common origin; (b) posterior cerebral and superior cerebellar arteries arise from a common origin; and (c) all pontine branches on one side arise from common origin.
Authors' note: Additional reference: Stehlbens, W.E. Aneurysms and anatomical variation of cerebral arteries. Arch. Pathol . 75:45-64, 1963.
Redrawn from McCullough, AN (Rewritten posthumously for the author by Howard K. Suzuki). Some anomalies of the arterial circle (of Willis) and related vessels. Anat. Rec. 142:537-543, 1962.
Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
Anatomy Atlases is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. 
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/